Eco Friendly – Phytoremediation
Phytoremediation Refers To The Technologies That Use Living Plants To Clean Up Soil, Air And Water Contaminated With Hazardous Contaminants. It Is Defined As “The Use Of Green Plants And The Associated Microorganisms Along With Proper Oil Amendments And Agronomic Techniques To Either Contain, Removes Or Render Toxic Environmental Contaminants Harmless.”
Phytoremediation May Be Applied To Polluted Soil Or Static Water Environment. Examples Where Phytoremediation Has Been Used Successfully Include The Restoration Of Abandoned Metal Mine Workings And Sites Where Polychlorinated Biphenyl Shave Been Dumped During Manufacture And Mitigation Of On-going Coalmine Discharges Reducing The Impact Of Contaminants In Soils, Water Or Air.
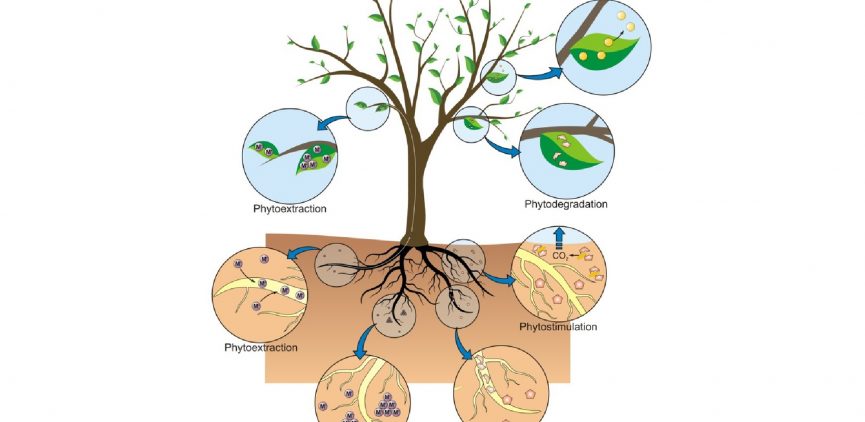
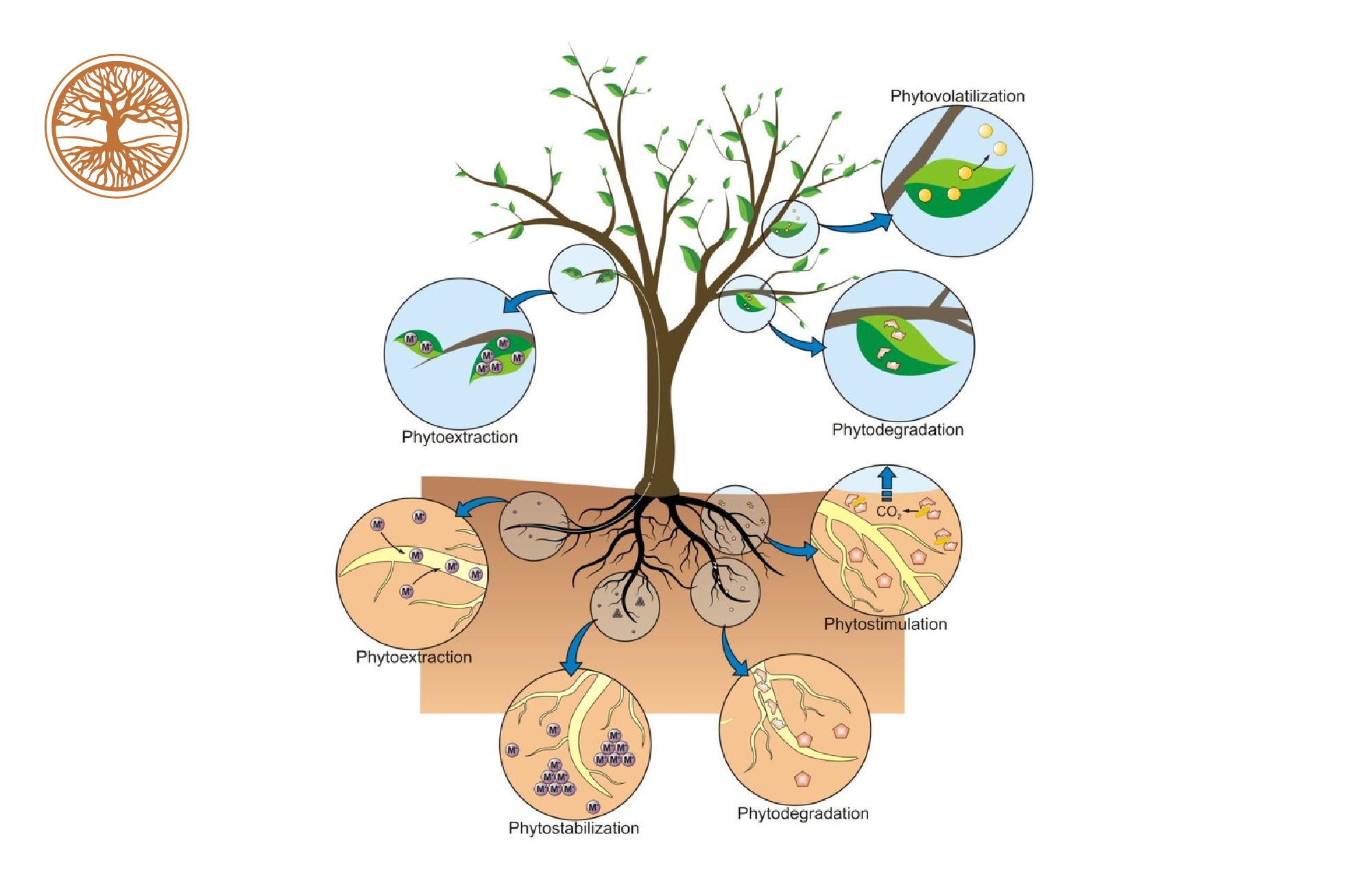
Different Phytoremediation Process
- Phytoextraction
- Phytostabilisation
- Phytodegradation
- Phytostimulation
- Phytovolatilisation
- Phytoscreening
- Phytotransformation
- Rhizofiltration
- Phytodesalinisationt
- Biological Hydraulic Containment
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row]